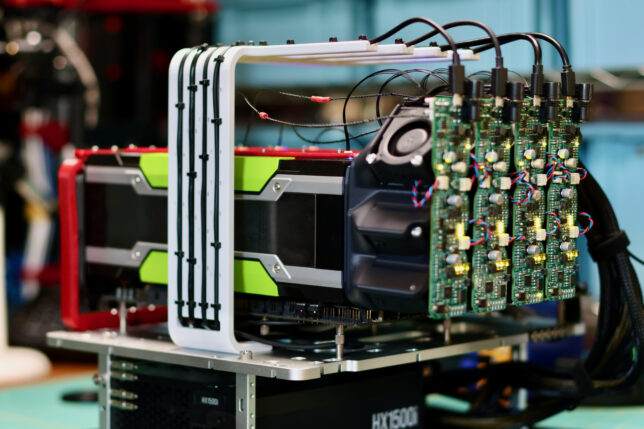
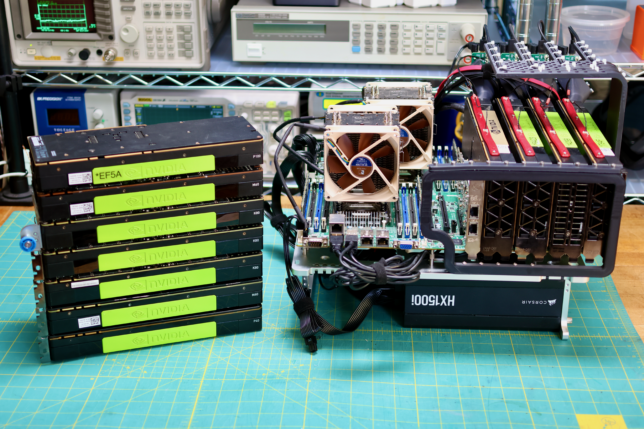
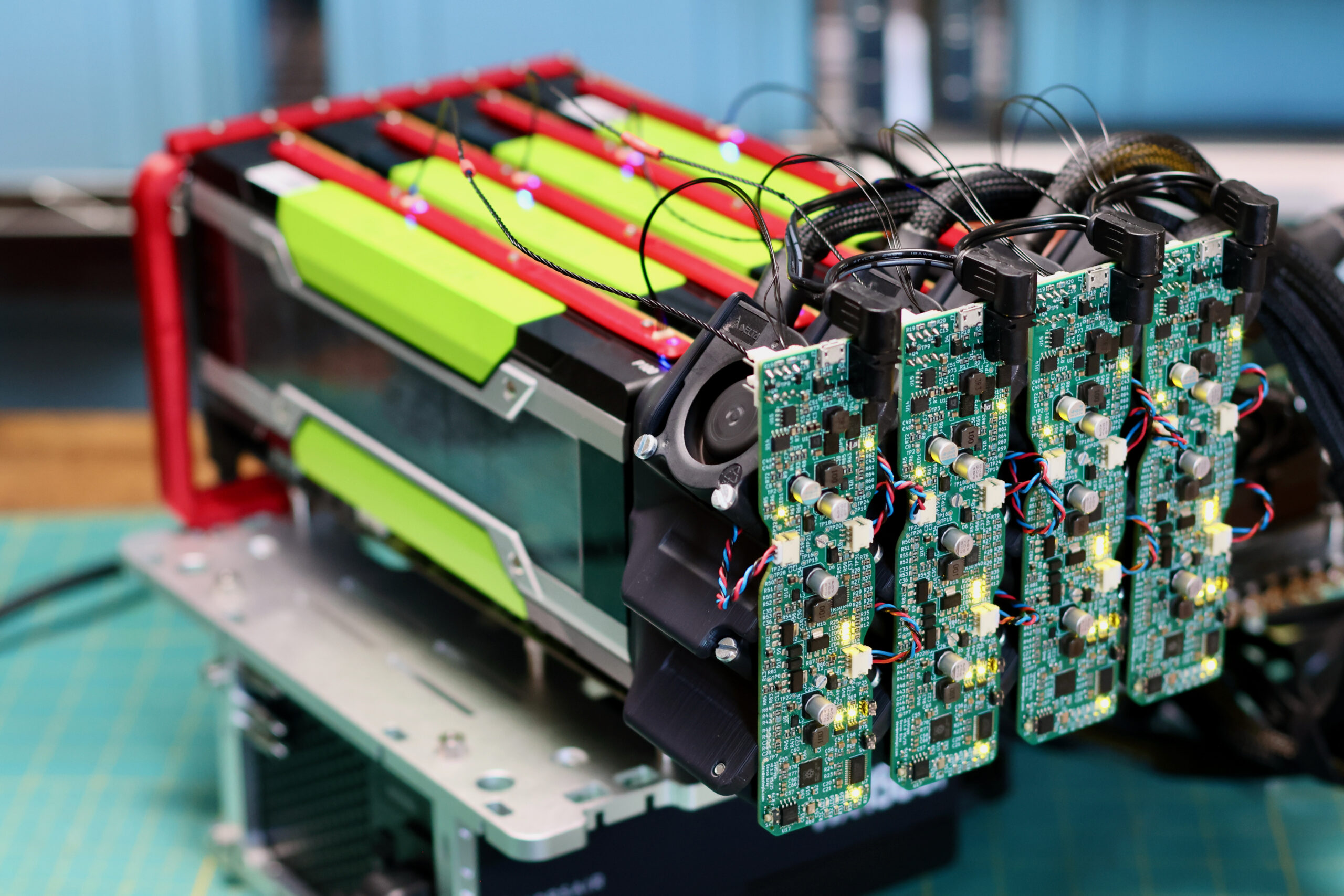
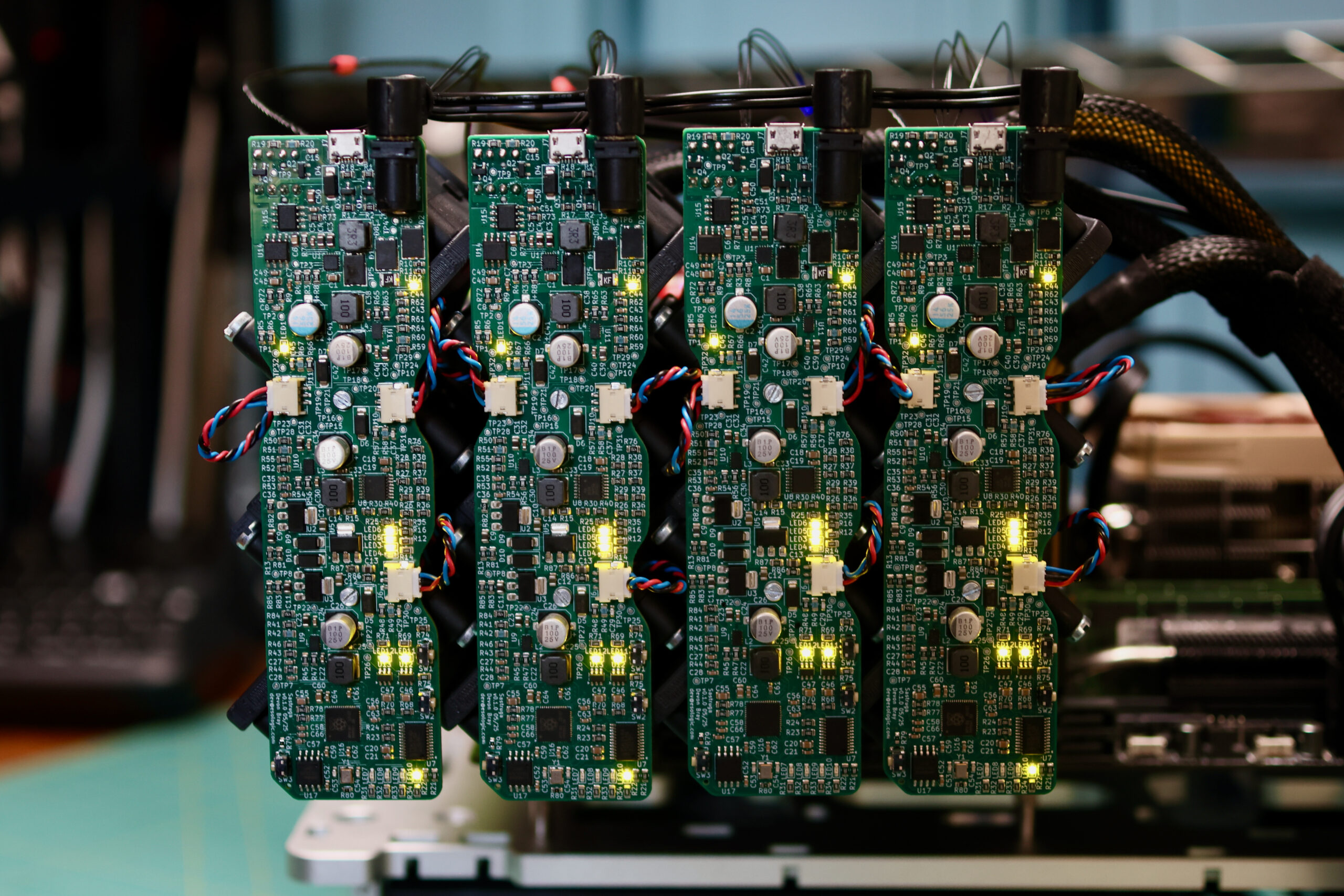
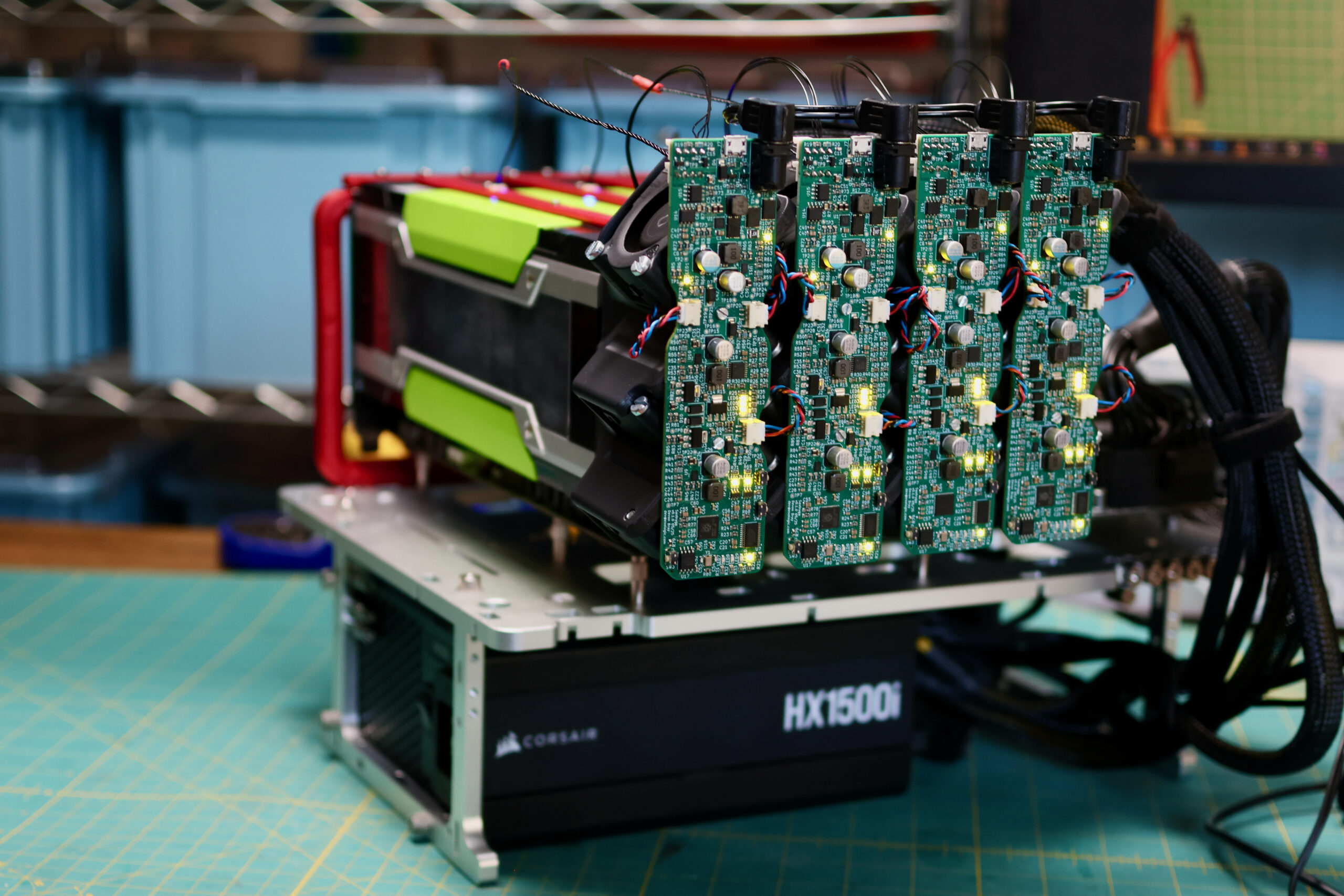
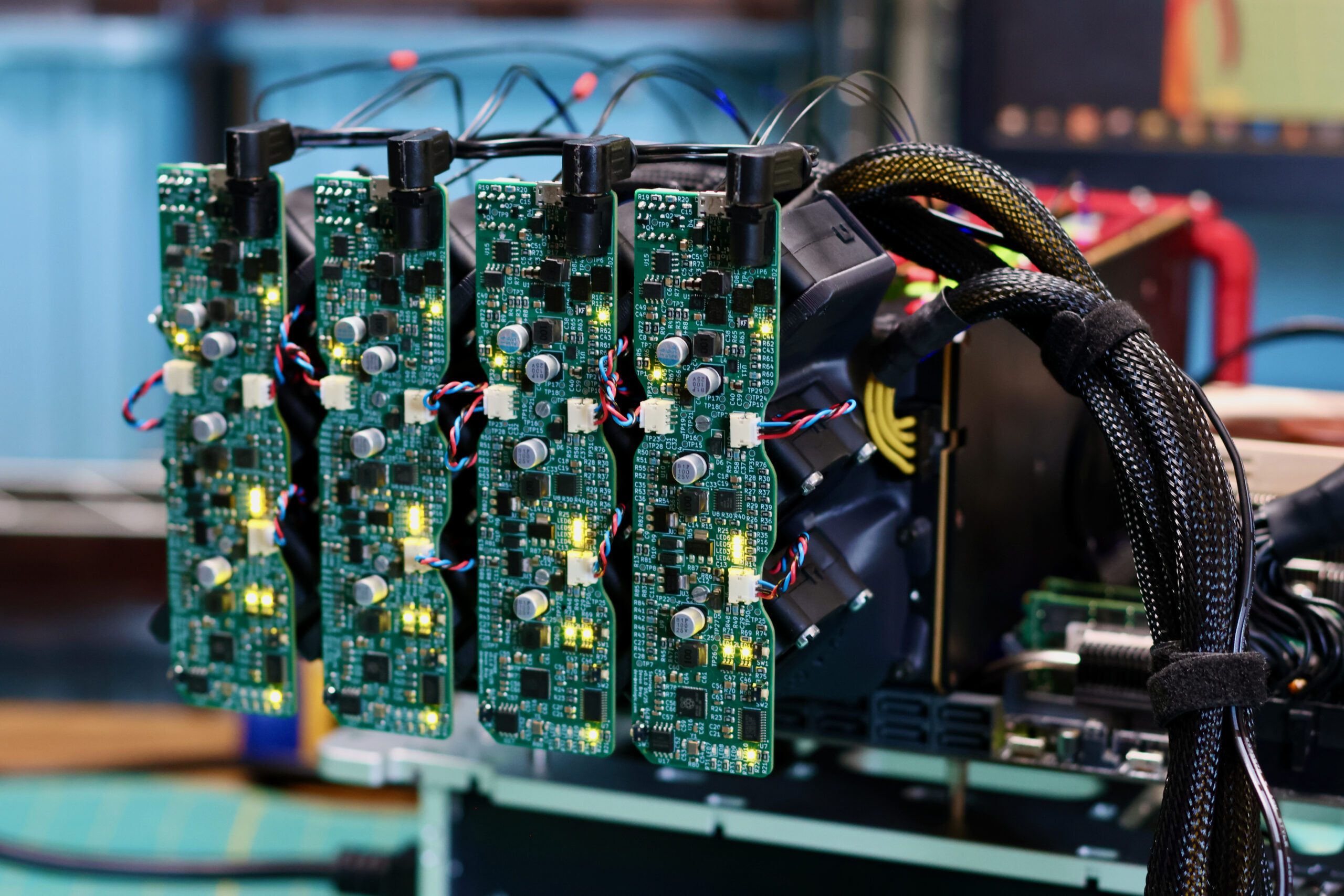
Previously a plan was set in motion to benchmark my collection of mighty Tesla GPUs. The set of cooler manifolds are designed, a GPU server benchmark suite has been created, and the time has come to start working through the spreadsheet. I have long suspected that the older multi node cards could be fantastic for image processing. Finally we can quantify how much life is left in these older cards.
Tag: python
First look at the New GPU Cooler Prototype
For the past while I’ve been working on a major redesign of my high performance gpu cooler project.
The rapid ascent of the LLM into the collective consciousness has sent the big players into a frenzy over datacenter GPUs. This is putting accelerating downward pressure on the price of all used compute GPUs, even the historically pricey stuff. P100s can be had for ~$100, V100 16GB are selling for ~$500, any day now the lower VRAM Ampere cards are going to drop below $1000…
We need a new cooler that can support any of these 300W GPUs, can be installed as densely as the cards, and is easy on the ears for homelab use. Pictured below are four prototype coolers installed on Tesla P100s:
Won Pound by Won Pound is released!
This post is one in a series about GANce
Close-readers, twitter-followers and corporeal-comrades will have already beheld the good news that Won Pound by Won Pound has been released! This is Won’s second album-length project (first of course being Post Space released in 2018), and graces listener’s ears courtesy of Minaret Records, a California jazz label.
The record is accompanied by an album-length music video synthesized with GANce, containing a completely unique video for each track. These 93960 frames have been the ultimate goal of this project since it’s inception, and serve as the best demonstration as to what GANce can do. Within the video (linked below), the video for ‘buzzz’ is a personal favorite, demonstrating the three core elements of a projection file blend:
GANce Overlays
This post is one in a series about GANce
As it stood, the three main features that would comprise the upcoming collaboration with Won Pound (slated for release mid-April) were:
- Projection Files (using a styleGAN2 network to project each of the individual frames in a source video, resulting in a series of latent vectors that can be manipulated and fed back into the network to create synthetic videos)
- Audio Blending (using alpha compositing to combine a frequency domain representation of an audio signal with a series of projected vectors)
- Network Switching (feeding the same latent vector into multiple networks produced in the same training run, resulting in visually similar results)
As detailed in the previous post. The effect of these three features can be seen in this demo:
Knowing we had enough runway to add another large feature to the project, and feeling particularly inspired following a visit to Clifford Ross’ exhibit at the Portland Museum of Art, I began exploring the relationship between the projection source video and the output images synthesized by the network.
High performance GPU cooler for the NVIDIA Tesla K80
Edit: This project was completed hackathon-style in a matter of days. I’ve been working to optimize the design and sell kits, follow along here.
Here’s a (long winded) video overview of this project:
Background
Rendered desperate for VRAM by a forthcoming now released! stylegan-related project, I recently had to wade thermistor first into the concernedly hot and strange world of GPUs without video outputs to design a high performance cooler for the NVIDIA Tesla K80.
Too esoteric to game on, and too power hungry to mine cryptocurrencies with, the K80 (allegedly the ‘The World’s Most Popular GPU’) can be had for under $250 USD on ebay, a far cry from it’s imperial MSRP of $5000. By my math, the card is one of the most cost-efficient ways to avail one’s self of video ram by the dozen of gigabytes.
This sounds great on paper, but actually getting one of these configured to do useful work is a kind of a project in, and of itself. I’ll eventually get to this in the aforementioned upcoming post. Today’s topic however, is upstream of all that: the task of keeping these things cool.
Quickly drawing grids of rectangles, and updating their colors with VisPy
Here’s a demo run of the code:
Background
From the VisPy website:
VisPy is a Python library for interactive scientific visualization that is designed to be fast, scalable, and easy to use.
While looking for a near real time data visualization alternative to the venerable matplotlib, I came across this jaw dropping demo:
Absolutely insane, achieving that kind of performance in python is amazing to say the least. This demo in particular seems like it would be more likely to come from a pygame application at the least, but looks more like it would be a Unity project.
The VisPy project is massive, but luckily, there is a set of really good examples included in the repo. Reminds me of the Arduino standard library in this way. After through all of running these, I didn’t find exactly what I was looking for.
For how simple the finished product looks, the learning curve on the way there was surprisingly steep. Hopefully this post saves you some time.
How to host private Python packages on Bitbucket for free, AND how to use them in a circleci pipeline
Background
pip install git+ssh://git@bitbucket.org/esologic/sample_project.git
pip install git+ssh://git@bitbucket.org/esologic/sample_project.git@master # on the master branch pip install git+ssh://git@bitbucket.org/esologic/sample_project.git@0.0.2 # on the version tag of 0.0.2
(venv) dev@ESO-3:/tmp$ pip install git+ssh://git@bitbucket.org/esologic/sample_project.git Collecting git+ssh://git@bitbucket.org/esologic/sample_project.git Cloning ssh://git@bitbucket.org/esologic/sample_project.git to ./pip-sjec1gbh-build git@bitbucket.org: Permission denied (publickey). fatal: Could not read from remote repository. Please make sure you have the correct access rights and the repository exists. Command "git clone -q ssh://git@bitbucket.org/esologic/sample_project.git /tmp/pip-sjec1gbh-build" failed with error code 128 in None
Using private repo packages locally
Step 1: Make sure your repo CAN be installed as a python package
setup.py file. Here are best the best set of docs I’ve found on how to make this file.setup.py. This repo will also be the standard example for this post.sample_project as an example, we can do this like so:(venv) dev@ESO-3:/tmp$ pip install /mnt/c/Users/dev/Documents/misc_git/sample_project/ Processing /mnt/c/Users/dev/Documents/misc_git/sample_project Installing collected packages: sample-project Running setup.py install for sample-project ... done Successfully installed sample-project-1.0 (venv) dev@ESO-3:/tmp$ python Python 3.6.8 (default, Jan 14 2019, 11:02:34) [GCC 8.0.1 20180414 (experimental) [trunk revision 259383]] on linux Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information. >>> from sample_project import print_quote >>> print_quote() If they can get you asking the wrong questions, they don't have to worry about answers. >>>
If your package behaves as expected when installed like this locally, you’re all set to push the changes to your bitbucket repo and continue with the rest of the guide.
Step 2: Create SSH keys and add them to bitbucket
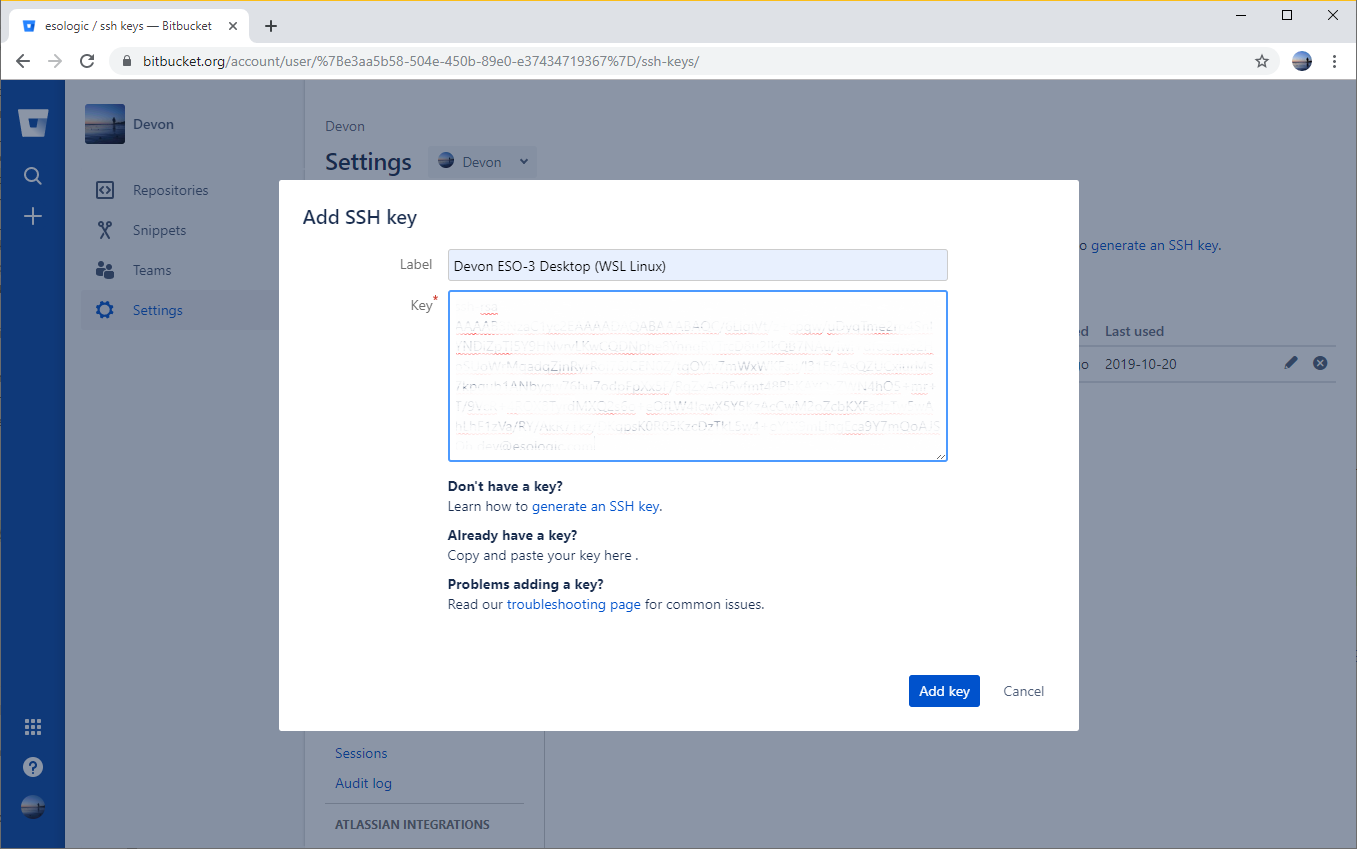
dev@esologic.com. Make sure whenever you see that, to substitute email address associated with your bitbucket account.~/.ssh. If you don’t see both id_rsa and id_rsa.pub files in that directory, create them with:ssh-keygen -m PEM -t rsa -C "dev@esologic.com"
passphrase blank.Windows steps to create ssh keys
$ ssh-keygen -m PEM -t rsa -C "dev@esologic.com" -E md5 $ cd C:\Users\dev\.ssh $ ssh-add id_rsa $ ssh -T git@bitbucket.org
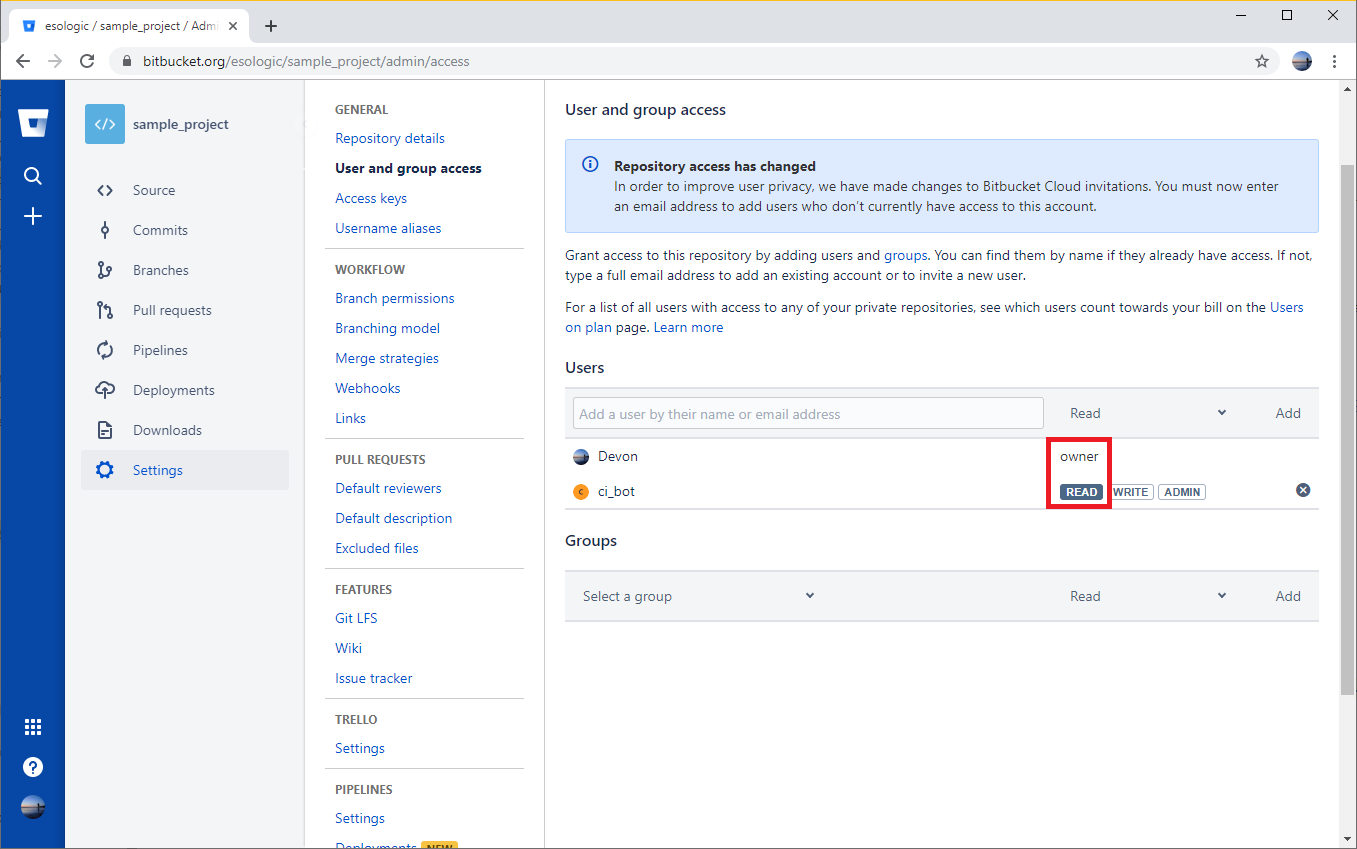
Step 3: Make sure your account can read from the private repo with your python package
Devon account is an owner of the repo, it will be allowed to read from the repo. The account ci_bot will also be able to read from the repo because it has read permissions.Step 4: Install the package from bitbucket
(venv) dev@ESO-3:/tmp$ pip install git+ssh://git@bitbucket.org/esologic/sample_project.git Collecting git+ssh://git@bitbucket.org/esologic/sample_project.git Cloning ssh://git@bitbucket.org/esologic/sample_project.git to ./pip-nkrqsxao-build setsockopt IPV6_TCLASS 8: Operation not permitted: Installing collected packages: sample-project Running setup.py install for sample-project ... done Successfully installed sample-project-1.0 (venv) dev@ESO-3:/tmp$ python Python 3.6.8 (default, Jan 14 2019, 11:02:34) [GCC 8.0.1 20180414 (experimental) [trunk revision 259383]] on linux Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information. >>> import sample_project >>> sample_project.print_quote() If they can get you asking the wrong questions, they don't have to worry about answers. >>>
Fantastic! Remember, your pip command git+ssh://git@bitbucket.org/esologic/sample_project.git will be different for your package. It will look something like this: git+ssh://git@bitbucket.org/{your username}/{your project}.git.
Using private repo packages in circleci
Step 5: Create a “machine user” in bitbucket
sample_project repo.Step 6: Create SSH keys and add them to your machine user’s account
On whatever you system you have been using so far, enter the following commands and remember to leave passphrase blank.
mkdir ~/.ssh/ci_bot_keys ssh-keygen -m PEM -t rsa -C "ci_bot@example.com" -f ~/.ssh/ci_bot_keys/id_rsa
Add the contents of ~/.ssh/ci_bot_keys/id_rsa.pub to bitbucket while signed in as your machine user like we did in step 2.
Step 7: Try git+ssh key insertion locally
(Note: you can skip this step, but if things don’t work when you add the step to your CI build start looking for errors here.)
GIT_SSH_COMMAND you can select which SSH key gets used by pip when doing an ssh pull.export SSH_AUTH_SOCK=none export GIT_SSH_COMMAND='ssh -i ~/.ssh/ci_bot_keys/id_rsa'
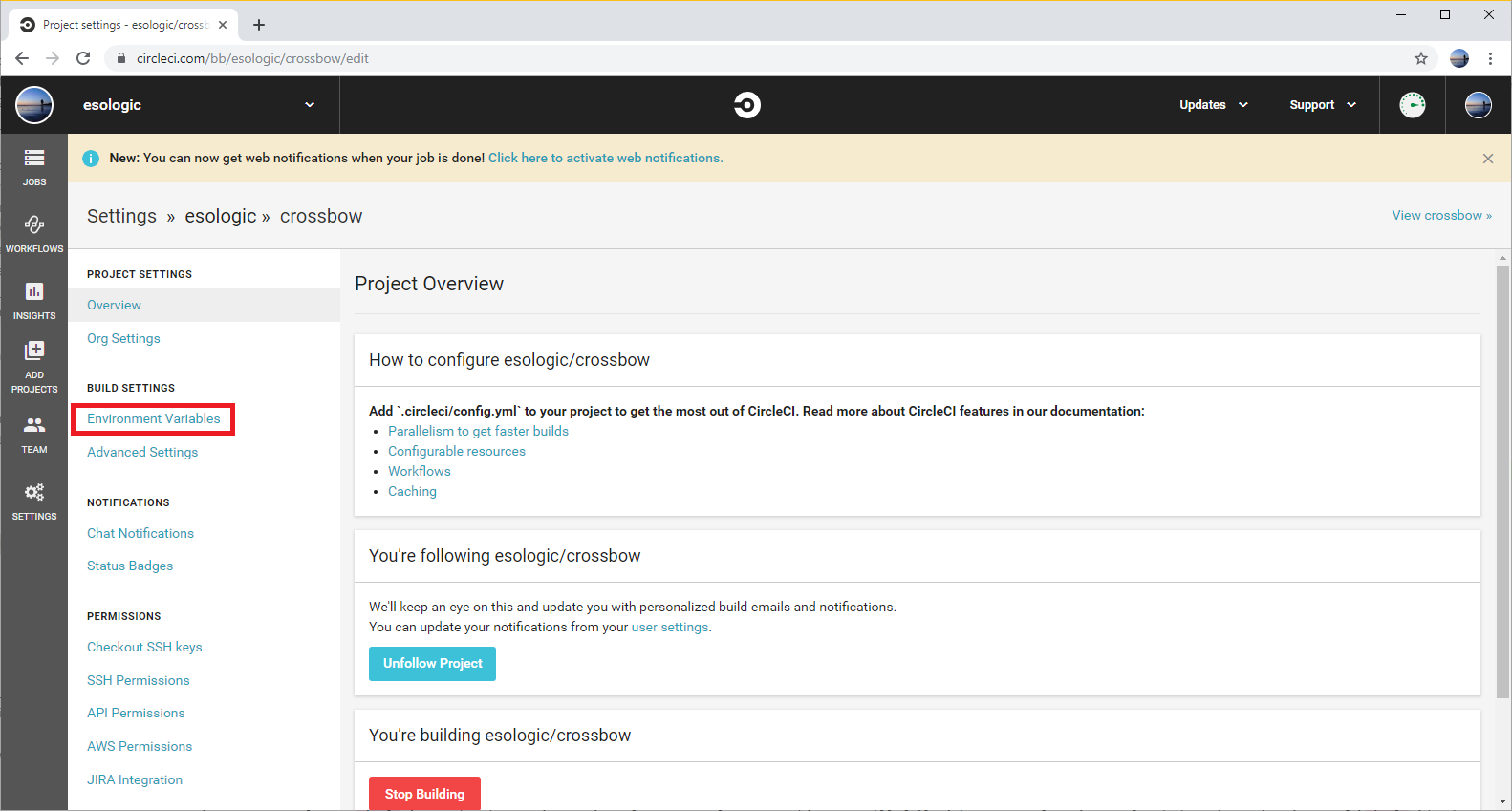
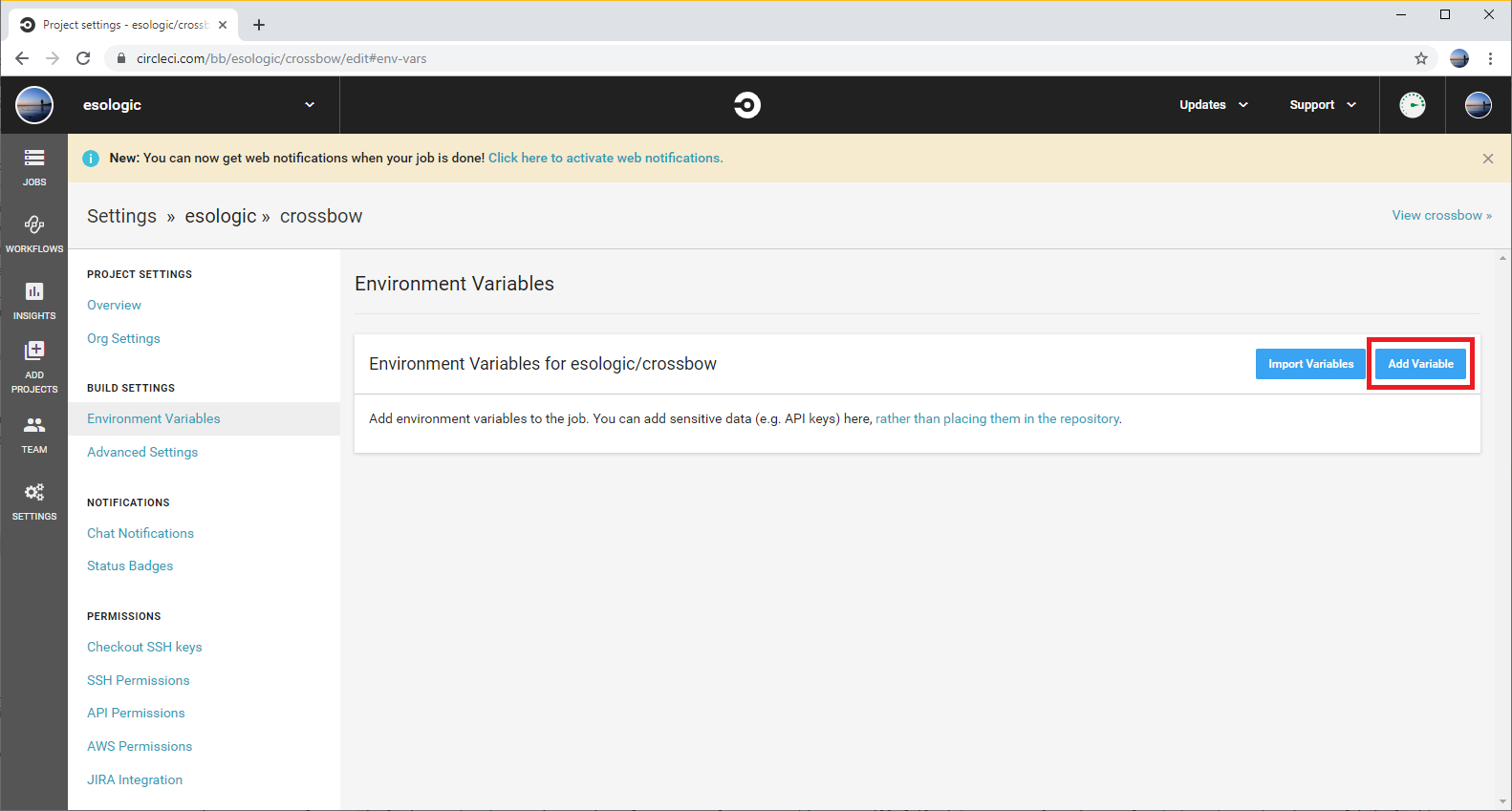
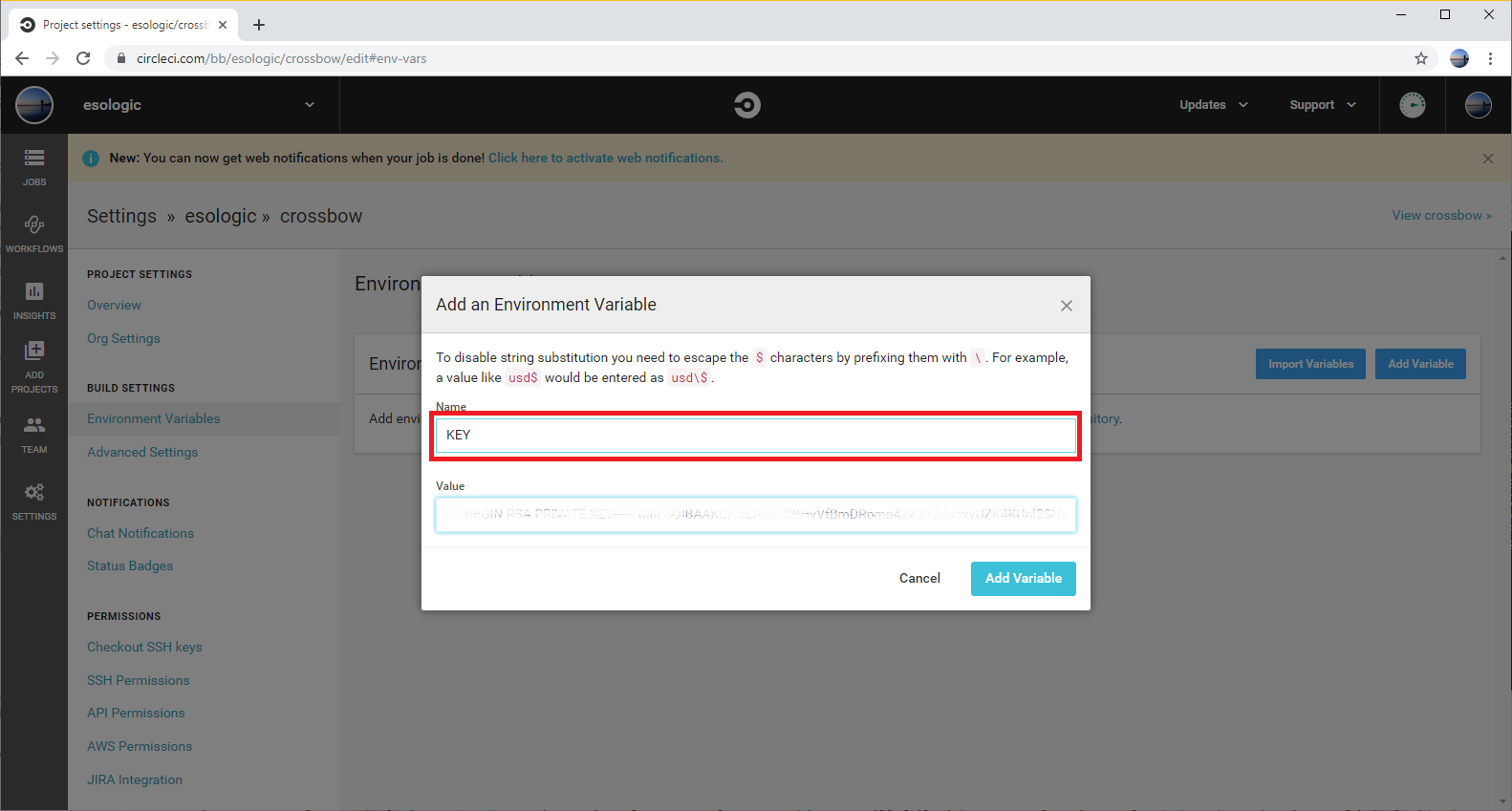
Step 8: Set the `$KEY` environment variable in circleci
~/.ssh/ci_bot_keys/id_rsa) available to the circle build process.(venv) dev@ESO-3:/tmp$ cat ~/.ssh/ci_bot_keys/id_rsa | tr "\n" "_"
-----END RSA PRIVATE KEY-----_ in case your terminal doesn’t wrap correctly.sample_project) in.crossbow is the name of my project.Now that the variable is set, we need to change our circle config to use it.
Step 9: Add the step to your /.circleci/config.yml file
You have to make sure that the export GIT_SSH_COMMAND step happens in the same step as any pip commands. Your full dependencies installation circle step may look something like this:
- run:
name: Install Dependencies
command: |
# Give us access to private repos
export KEY_PATH=tmp_id_rsa
echo -e "${KEY//_/\\n}" > $KEY_PATH
chmod 600 $KEY_PATH
export SSH_AUTH_SOCK=none
export GIT_SSH_COMMAND='ssh -i $KEY_PATH'
python3 -m venv venv
. venv/bin/activate
pip install -r ./requirements.txtts.txt
Make sure you select a circle image that has a git version of 2.17.0 or later, or this step will fail without an explanation. I found that the python image of circleci/python:3.7-buster worked when testing.
Thanks to
- http://redgreenrepeat.com/2018/05/25/specifying-different-ssh-key-for-git/
Play multiple sound files on multiple output devices with Python and sounddevice
Ever wanted to have multiple different sound files playing on different output devices attached to a host computer? Say you’re writing a DJing application where you want one mix for headphones and one for the speakers. Or you’re doing some sort of kiosk or art installation where you have many sets of speakers that need to all be playing their own sound file but the whole thing needs to be synchronized. This would even be cool for something like an escape room.
The ladder example is where I needed this bit of code. I’ve been working with interdisciplinary artist Sara Dittrich on a few projects recently and she asked if I could come up with a way to play 8 different mono sound files on 8 different loudspeakers. Here’s a video of the whole setup in action, and an explanation of the project:
I’ve wrapped up all of the code for the art installation project, and that can be found in a github repo here. It includes the startup functionality etc. If you’re interested in recreating the video above, that repo would be a good starting place. The following is a list of the parts used to make that build happen:
Multi-Audio Example
It is worth it to give a simple example of how to play multiple files on multiple audio devices using python. I couldn’t find an examples on how to do this online and had to spend some time experimenting to make it all come together. Hopefully this saves you the trouble.
To install sounddevice on my Raspberry Pi, I had to run the following commands:
sudo apt-get install python3-pip python3-numpy libportaudio2 libsndfile1 libffi-dev python3 -m pip install sounddevice soundfile
For this example, let’s say there are 4 audio files in the same directory as multi.py , so the directory looks like this:
multi_audio/ ├── 1.wav ├── 2.wav ├── 3.wav ├── 4.wav └── multi.py
The code is based on the sounddevice library for python, whose documentation is pretty sparse. This script will find the audio files, and then play them on as many devices as there are attached. For example, if you have 3 sound devices it will play 1.wav, 2.wav and 3.wav on devices 1-3. If you have any questions, feel free to ask:
"""
multi.py, uses the sounddevice library to play multiple audio files to multiple output devices at the same time
Written by Devon Bray (dev@esologic.com)
"""
import sounddevice
import soundfile
import threading
import os
DATA_TYPE = "float32"
def load_sound_file_into_memory(path):
"""
Get the in-memory version of a given path to a wav file
:param path: wav file to be loaded
:return: audio_data, a 2D numpy array
"""
audio_data, _ = soundfile.read(path, dtype=DATA_TYPE)
return audio_data
def get_device_number_if_usb_soundcard(index_info):
"""
Given a device dict, return True if the device is one of our USB sound cards and False if otherwise
:param index_info: a device info dict from PyAudio.
:return: True if usb sound card, False if otherwise
"""
index, info = index_info
if "USB Audio Device" in info["name"]:
return index
return False
def play_wav_on_index(audio_data, stream_object):
"""
Play an audio file given as the result of `load_sound_file_into_memory`
:param audio_data: A two-dimensional NumPy array
:param stream_object: a sounddevice.OutputStream object that will immediately start playing any data written to it.
:return: None, returns when the data has all been consumed
"""
stream_object.write(audio_data)
def create_running_output_stream(index):
"""
Create an sounddevice.OutputStream that writes to the device specified by index that is ready to be written to.
You can immediately call `write` on this object with data and it will play on the device.
:param index: the device index of the audio device to write to
:return: a started sounddevice.OutputStream object ready to be written to
"""
output = sounddevice.OutputStream(
device=index,
dtype=DATA_TYPE
)
output.start()
return output
if __name__ == "__main__":
def good_filepath(path):
"""
Macro for returning false if the file is not a non-hidden wav file
:param path: path to the file
:return: true if a non-hidden wav, false if not a wav or hidden
"""
return str(path).endswith(".wav") and (not str(path).startswith("."))
cwd = os.getcwd()
sound_file_paths = [
os.path.join(cwd, path) for path in sorted(filter(lambda path: good_filepath(path), os.listdir(cwd)))
]
print("Discovered the following .wav files:", sound_file_paths)
files = [load_sound_file_into_memory(path) for path in sound_file_paths]
print("Files loaded into memory, Looking for USB devices.")
usb_sound_card_indices = list(filter(lambda x: x is not False,
map(get_device_number_if_usb_soundcard,
[index_info for index_info in enumerate(sounddevice.query_devices())])))
print("Discovered the following usb sound devices", usb_sound_card_indices)
streams = [create_running_output_stream(index) for index in usb_sound_card_indices]
running = True
if not len(streams) > 0:
running = False
print("No audio devices found, stopping")
if not len(files) > 0:
running = False
print("No sound files found, stopping")
while running:
print("Playing files")
threads = [threading.Thread(target=play_wav_on_index, args=[file_path, stream])
for file_path, stream in zip(files, streams)]
try:
for thread in threads:
thread.start()
for thread, device_index in zip(threads, usb_sound_card_indices):
print("Waiting for device", device_index, "to finish")
thread.join()
except KeyboardInterrupt:
running = False
print("Stopping stream")
for stream in streams:
stream.abort(ignore_errors=True)
stream.close()
print("Streams stopped")
print("Bye.")
Here are some more photos of the build:
Why you should use Processes instead of Threads to isolate loads in Python
Key Learning
Python uses a Global Interpreter Lock to make sure that memory shared between threads isn’t corrupted. This is a design choice of the language that has it’s pros and cons. One of these cons is that in multi-threaded applications where at least one thread applies a large load to the CPU, all other threads will slow down as well.
For multi-threaded Python applications that are at least somewhat time-sensitive, you should use Processes over Threads.
Experiment
I wrote a simple python script to show this phenomenon. Let’s take a look.
def increment(running_flag, count_value):
c = 0
while True:
if not running_flag.value:
break
count_value.value = c # setting a Value is atomic
c += 1
The core is this increment function. It takes in a Value and then sets it over and over, increment each loop, until the running_flag is set to false. The value of count_value is what is graphed later on, and is the measure of how fast things are going.
The other important bit is the load function:
def load(running_flag):
z = 10
while True:
if not running_flag.value:
break
z = z * z
Like increment, load is the target of a thread or process. The z variable quickly becomes large and computing the loop becomes difficult quickly.
The rest of the code is just a way to have different combinations of increment and load running at the same time for varying amounts of time.
Result
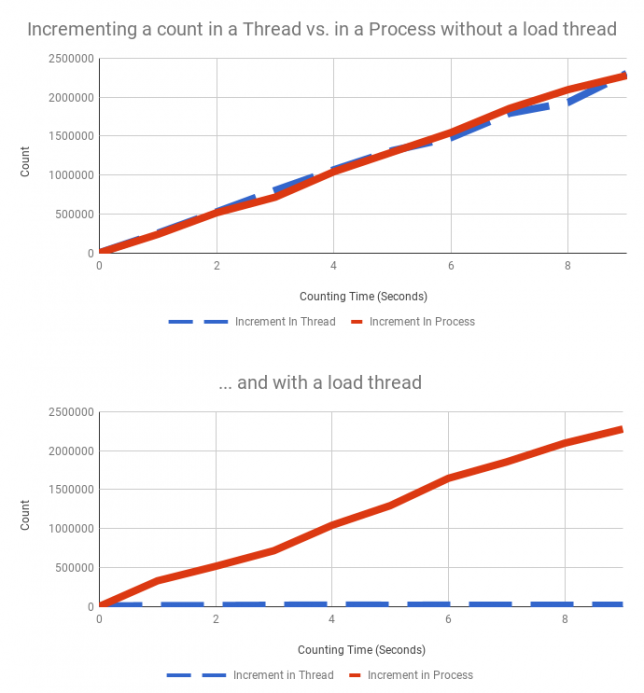
The graph really tells the story. Without the load thread running, the process and thread versions of increment run at essentially the same rate. When the load thread is running, increment in a thread grinds to a halt compared to the process which is unaffected.
That’s all! I’ve pasted the full source below so you can try the experiment yourself.
from multiprocessing import Process, Value
from threading import Thread
from time import sleep
from ctypes import c_bool, c_longdouble
def increment(running_flag, count_value):
"""
Increment the value in count_value as quickly as possible. If running_flag is set to false, break out of the loop
:param running_flag: a multiprocessing.Value boolean
:param count_value: a multiprocessing.Value Long Double
"""
c = 0
while True:
if not running_flag.value:
break
count_value.value = c # setting a Value is atomic
c += 1
def load(running_flag):
"""
Apply a load to the CPU. If running_flag is set to false, break out of the loop
:param running_flag: a multiprocessing.Value boolean
"""
z = 10
while True:
if not running_flag.value:
break
z = z * z
def mct(target, flag, value):
"""
Returns a lambda that can be called to get a thread to increment a increment using a thread
"""
return lambda: Thread(target=target, args=(flag, value))
def mcp(target, flag, value):
"""
Returns a lambda that can be called to get a thread to increment a increment using a process
"""
return lambda: Process(target=target, args=(flag, value))
def mlt(target, flag):
"""
Returns a lambda that can be called to get a thread that will load down the CPU
"""
return lambda: Thread(target=target, args=(flag,))
if __name__ == "__main__":
f = Value(c_bool, True) # control flag, will be passed into child thread/process so they can be stopped
cv = Value(c_longdouble, 0) # increment value
child_lists = [mct(increment, f, cv)], [mcp(increment, f, cv)], [mct(increment, f, cv), mlt(load, f)], [mcp(increment, f, cv), mlt(load, f)]
for delay in range(10): # maximum run time of 10 seconds
max_counts = []
for get_children in child_lists:
# reset the flag and increment
f.value = True
cv.value = 0
# the child thread/processes will end up in here
children = []
for get_child in get_children:
child = get_child() # create a new instance of the thread/process to be launched
child.start()
children.append(child)
sleep(delay)
f.value = False
for child in children:
child.join() # stop the process
max_counts.append(cv.value)
s = ""
for count in max_counts:
s += str(count) + " "
print(s)
CHAMP: Compliant Hook Arboreal Mobility Platform (Senior Thesis Project)
For my senior thesis project at WPI, myself and two colleagues (Rachael Putnam – RBE/ME and Mead Landis – RBE/ME) designed a tree climbing robot. I was in charge of designing and implementing the electronics and controls software. I was the most intense project I have ever worked on, both in terms of difficulty and potential impact. Here is our poster for project presentation day:
Here’s a video of the prototype climbing:
We did a blog during the project, here is the best post I wrote:
The report is massive, check it out here: https://digital.wpi.edu/concern/student_works/s4655j16f?locale=en