So here’s a video:
So pretty easy but important step here. For a while I’ve known that I need to have some more feedback from the robot that just LED brightness levels on the controller. This VB program allows me to get analog values from the vehicle and interpret them in any number of ways. You can download and run that program HERE, and like I said in the video I’ve refrained from going open source with my VB programs in the past because they’ve never really had any polish to them. But now I think it will be good to keep this all open.
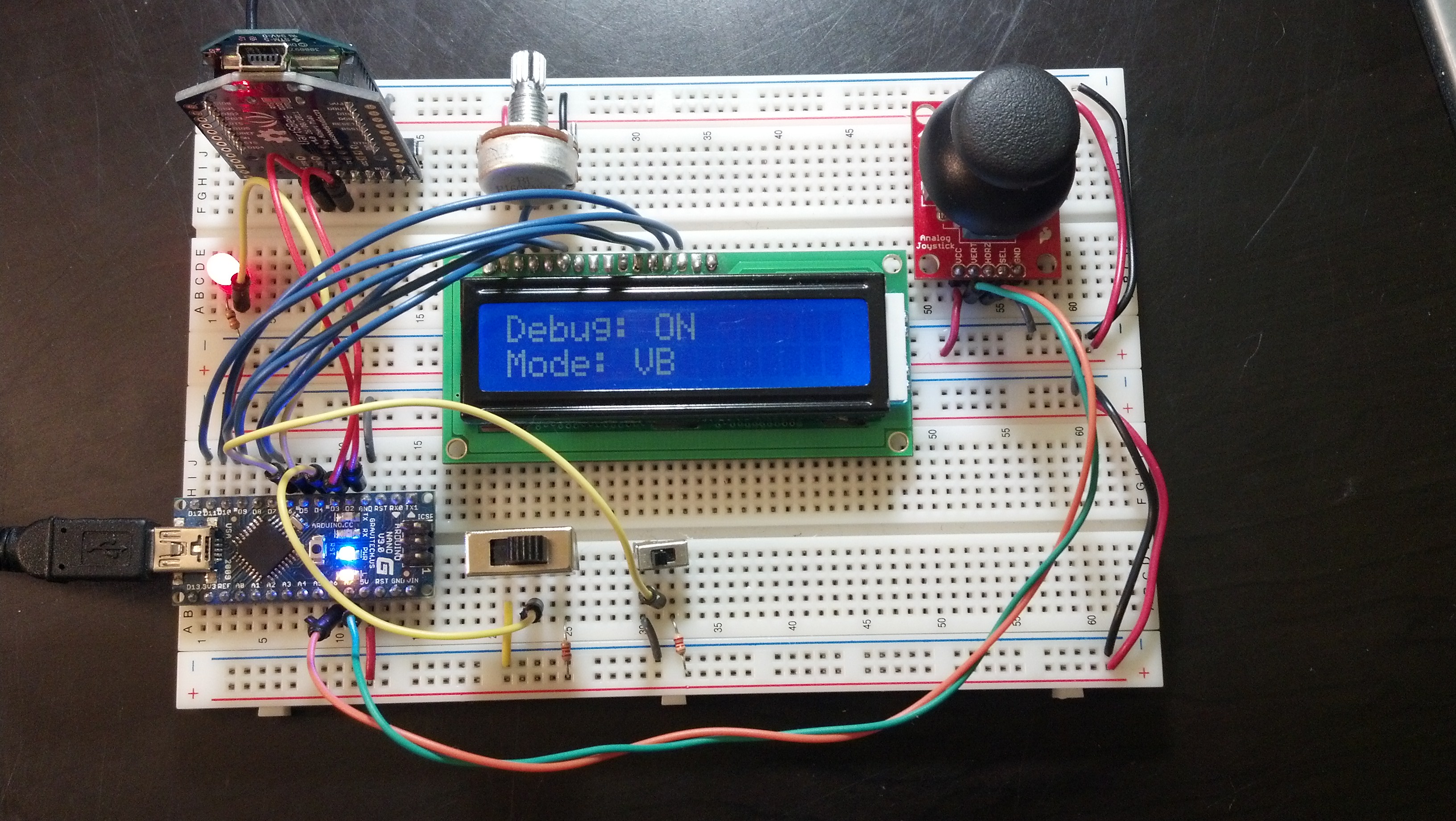
I also added a 16 * 2 character LCD to my controller. I’ve sacrificed the 6 pins because hopefully in the long run it will be a better experience for the user. I may go back, but for now I’d rather build around something that’s a little more constraining as it will force me to innovate a little bit more. Here’s a picture of the new controller:
Here’s the program:
//Serial Handshake declaration
#include <string.h> // we'll need this for subString
#define MAX_STRING_LEN 100 // like 3 lines above, change as needed.
const char EOPmarker = '.'; //This is the end of packet marker
char serialbuf[100]; //This gives the incoming serial some room. Change it if you want a longer incoming.
//SoftwareSerial declaration
#include <SoftwareSerial.h>
SoftwareSerial xbee_serial(2, 3);
//Shift Register Pins declaration
int SER_Pin = 5; //pin 14 on the 75HC595
int RCLK_Pin = 6; //pin 12 on the 75HC595
int SRCLK_Pin = 7; //pin 11 on the 75HC595
#define number_of_74hc595s 1 //How many of the shift registers - change this
#define numOfRegisterPins number_of_74hc595s * 8 //do not touch
boolean registers[numOfRegisterPins];
//Servo declarations
int left_servo_val;
int rght_servo_val;
//lcd declaration
#include <LiquidCrystal.h>
LiquidCrystal lcd(7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12);
//Misc Pin declaration
//inputs
int debug_switch1 = 4;
int debug_switch2 = 6;
//these values are for communication, not hardware inputs
int in_ref;
int in_brightness;
int in_pot1;
int in_pot2;
int in_accelerometer_x;
int in_accelerometer_y;
int in_accelerometer_z;
int in_temp1;
//outputs
//int pot_LED = 6;
int fade_LED = 5;
int debug_switch1_LED = 13;
//these values are for communication, not hardware outputs
int out_joystick_x;
int out_joystick_y;
//Misc Integer Declarations
int brightness = 0; // how bright the LED is
int fadeAmount = 51; // how many points to fade the LED by
int accel_x_min = 293;
int accel_x_max = 440;
int accel_y_min = 290;
int accel_y_max = 434;
void setup(){
Serial.begin(9600);
xbee_serial.begin(9600);
//shift register setup
pinMode(SER_Pin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(RCLK_Pin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(SRCLK_Pin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(0, INPUT);
clearRegisters();
writeRegisters();
//Misc Pin Declarations
pinMode(debug_switch1, INPUT);
pinMode(debug_switch2, INPUT);
//pinMode(pot_LED, OUTPUT);
pinMode(fade_LED, OUTPUT);
//lcd declaration
lcd.begin(16, 2);
xbee_serial.print("0,0,0."); // this is very important as it starts of the loop because it makes "xbee_serial.avalible() > 0.
}
void loop(){
if (xbee_serial.available() > 0) {
static int bufpos = 0;
char inchar = xbee_serial.read();
if (inchar != EOPmarker) {
serialbuf[bufpos] = inchar;
bufpos++;
}
else {
serialbuf[bufpos] = 0; //restart the buff
bufpos = 0; //restart the position of the buff
if (digitalRead(debug_switch1) == LOW){
digitalWrite(debug_switch1_LED, LOW); //LED in board indicates debug status
handshake();
lcd.setCursor(0, 0);
lcd.print("Debug: OFF");
lcd.setCursor(0, 1);
lcd.print(" ");
digitalWrite(debug_switch1_LED, LOW);
}
if (digitalRead(debug_switch1) == HIGH){
handshake(); //no matter what, the handshake happens normally
lcd.setCursor(0, 0);
lcd.print("Debug: ON ");
debug_handshake(); //the debug to console only slows the process downm no interference with data
digitalWrite(debug_switch1_LED, HIGH);
}
}
}
}
void handshake(){
//inputs, recived from vehicle
in_ref = atoi(subStr(serialbuf, "," , 1));
in_brightness = atoi(subStr(serialbuf, "," , 2));
in_pot1 = (map(atoi(subStr(serialbuf, "," , 3)),0,1023,0,255));
in_pot2 = atoi(subStr(serialbuf, "," , 4));
in_accelerometer_x = atoi(subStr(serialbuf, "," , 5));
in_accelerometer_y = atoi(subStr(serialbuf, "," , 6));
in_accelerometer_z = atoi(subStr(serialbuf, "," , 7));
in_temp1 = atoi(subStr(serialbuf, "," , 8));
analogWrite(fade_LED, in_brightness);
//analogWrite(pot_LED, in_pot1);
//outputs, sent to vehicle
brightness = brightness + fadeAmount;
// reverse the direction of the fading at the ends of the fade:
if (brightness == 0 || brightness == 255) {
fadeAmount = -fadeAmount ;
}
out_joystick_x = analogRead(7); //remap for coherency purposes
out_joystick_y = analogRead(6);
xbee_serial.print(brightness);
xbee_serial.print(",");
xbee_serial.print(out_joystick_x);
xbee_serial.print(",");
xbee_serial.print(out_joystick_y);
xbee_serial.print("."); //EOP marker
delay(10);
}
void debug_handshake() { //there are two debug modes
if (digitalRead(debug_switch2) == HIGH){
lcd.setCursor(0, 1);
lcd.print("Mode: 1 Line");
debug_handshake_fncy(); //this is good for looking at one line at a time (via the port monitor)
}
if (digitalRead(debug_switch2) == LOW){
debug_handshake_smpl(); //this is great for data interpretation (via VB)
lcd.setCursor(0, 1);
lcd.print("Mode: VB ");
}
}
void debug_handshake_fncy(){
Serial.print("INPUTS {");
Serial.print("refvolt: ");
Serial.print(in_ref);
Serial.print(",");
Serial.print(" fade: ");
Serial.print(brightness);
Serial.print(",");
Serial.print(" LED1: ");
Serial.print(in_pot1);
Serial.print(",");
Serial.print(" pot2: ");
Serial.print(in_pot2);
Serial.print(",");
Serial.print(" accel_x: ");
Serial.print(in_accelerometer_x);
Serial.print(",");
Serial.print(" accel_y: ");
Serial.print(in_accelerometer_y);
Serial.print(",");
Serial.print(" accel_z: ");
Serial.print(in_accelerometer_z);
Serial.print(",");
Serial.print(" temp1: ");
Serial.print(in_temp1);
Serial.print("}");
Serial.print(" | ");
Serial.print("OUTPUTS {");
Serial.print("joystick_x: ");
Serial.print(out_joystick_x);
Serial.print(",");
Serial.print(" joystick_y: ");
Serial.print(out_joystick_y);
Serial.print("}");
Serial.println("");
}
void debug_handshake_smpl(){ //just inputs seperated by commas then a | then outputs seperated by commas
Serial.print(in_ref);
Serial.print(",");
Serial.print(brightness);
Serial.print(",");
Serial.print(in_pot1);
Serial.print(",");
Serial.print(in_pot2);
Serial.print(",");
Serial.print(in_accelerometer_x);
Serial.print(",");
Serial.print(in_accelerometer_y);
Serial.print(",");
Serial.print(in_accelerometer_z);
Serial.print(",");
Serial.print(in_temp1);
Serial.print(",");
Serial.print("|");
Serial.print(out_joystick_x);
Serial.print(",");
Serial.print(out_joystick_y);
Serial.println("");
}
char* subStr (char* input_string, char *separator, int segment_number) { //for substring
char *act, *sub, *ptr;
static char copy[MAX_STRING_LEN];
int i;
strcpy(copy, input_string);
for (i = 1, act = copy; i <= segment_number; i++, act = NULL) {
sub = strtok_r(act, separator, &ptr);
if (sub == NULL) break;
}
return sub;
}
void clearRegisters(){ //for shift registers
for(int i = numOfRegisterPins - 1; i >= 0; i--){
registers[i] = LOW;
}
}
void writeRegisters(){ //for shift registers
digitalWrite(RCLK_Pin, LOW);
for(int i = numOfRegisterPins - 1; i >= 0; i--){
digitalWrite(SRCLK_Pin, LOW);
int val = registers[i];
digitalWrite(SER_Pin, val);
digitalWrite(SRCLK_Pin, HIGH);
}
digitalWrite(RCLK_Pin, HIGH);
}
//set an individual pin HIGH or LOW
void setRegisterPin(int index, int value){
registers[index] = value;
}
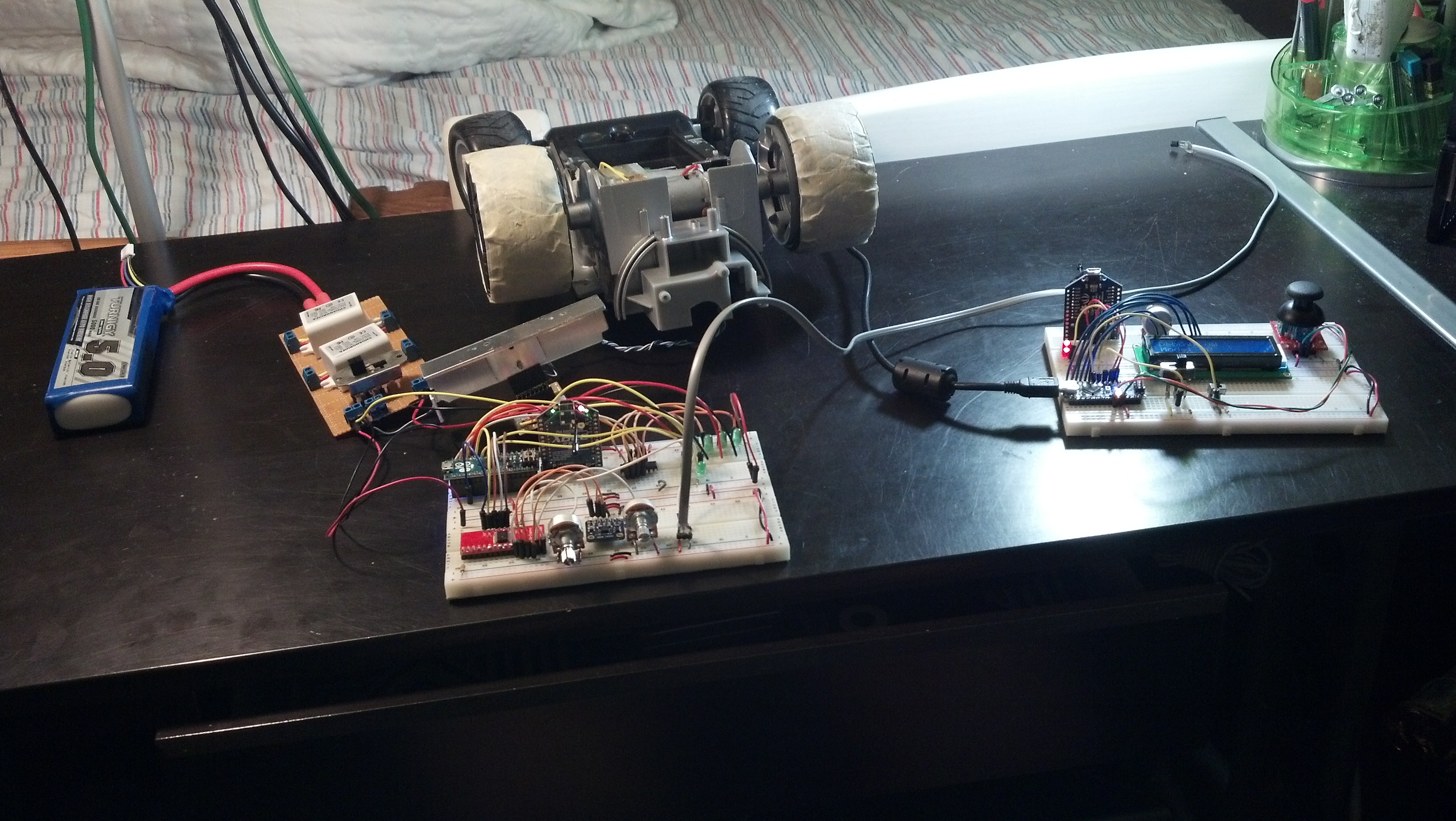
I didn’t mention in in the video, but I moved the mux from the controller, to the vehicle. It allows me to have 22 analog inputs, and the reason I took so long to finally add it was primarily laziness on my part. Aside from the the code is still very similar but close followers will notice that I cleaned up the way the program receives and sends code. It is much much more organized, and much more expandable. Here’s the “new” controller:
Here’s the new program:
//Serial Handshake declaration
#include <string.h> // we'll need this for subString
#define MAX_STRING_LEN 100 // like 3 lines above, change as needed.
const char EOPmarker = '.'; //This is the end of packet marker
char serialbuf[100]; //This gives the incoming serial some room. Change it if you want a longer incoming.
//SoftwareSerial declaration
#include <SoftwareSerial.h>
SoftwareSerial xbee_serial(8, 9);
//Mux control pins declarations
int s0 = 2;
int s1 = 3;
int s2 = 4;
int s3 = 7;
int SIG_pin = 0;
//Shift Register Pins declaration
int SER_Pin = 10; //pin 14 on the 75HC595
int RCLK_Pin = 11; //pin 12 on the 75HC595
int SRCLK_Pin = 12; //pin 11 on the 75HC595
#define number_of_74hc595s 1 //How many of the shift registers - change this
#define numOfRegisterPins number_of_74hc595s * 8 //do not touch
boolean registers[numOfRegisterPins];
//Servo declarations
#include <Servo.h>
Servo left_servo;
Servo rght_servo;
//Misc Pin declaration
//inputs
int debug_switch1 = 4;
//outputs
//these values are for communication, not hardware outputs
int out_ref;
int out_pot1;
int out_pot2;
int out_accelerometer_x;
int out_accelerometer_y;
int out_accelerometer_z;
int out_temp1;
int fade_LED = 13;
int x_LED = 5;
int y_LED = 6;
//int debug_switch1_LED = 12;
//Misc Integer declarations
int in_brightness;
int in_joystick_x;
int in_joystick_y;
int brightness = 0; // how bright the LED is
int fadeAmount = 51; // how many points to fade the LED by
int x_upperTrigger = 600;
int x_lowerTrigger = 450;
int y_upperTrigger = 600;
int y_lowerTrigger = 400;
void setup(){
Serial.begin(9600);
xbee_serial.begin(9600);
//mux setup
pinMode(s0, OUTPUT);
pinMode(s1, OUTPUT);
pinMode(s2, OUTPUT);
pinMode(s3, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(s0, LOW);
digitalWrite(s1, LOW);
digitalWrite(s2, LOW);
digitalWrite(s3, LOW);
//shift register setup
pinMode(SER_Pin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(RCLK_Pin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(SRCLK_Pin, OUTPUT);
clearRegisters();
writeRegisters();
//misc pin declarations
pinMode(x_LED, OUTPUT);
pinMode(y_LED, OUTPUT);
pinMode(fade_LED, OUTPUT);
xbee_serial.print("0,0,0."); // this is very important as it starts of the loop because it makes "xbee_serial.avalible() > 0.
}
void loop(){
if (xbee_serial.available() > 0) {
static int bufpos = 0;
char inchar = xbee_serial.read();
if (inchar != EOPmarker) {
serialbuf[bufpos] = inchar;
bufpos++;
}
else {
serialbuf[bufpos] = 0; //restart the buff
bufpos = 0; //restart the position of the buff
handshake();
setRegisterPin(1, HIGH);
writeRegisters();
}
}
}
void handshake(){
//inputs
in_brightness = atoi(subStr(serialbuf, "," , 1));
in_joystick_x = atoi(subStr(serialbuf, "," , 2));
in_joystick_y = atoi(subStr(serialbuf, "," , 3));
analogWrite(fade_LED,in_brightness);
if (in_joystick_x > x_upperTrigger){ //the below boolean blocks set pins high or low
setRegisterPin(4,HIGH);
setRegisterPin(5,LOW);
analogWrite(x_LED, map(in_joystick_x,x_upperTrigger,1023,0,255));
writeRegisters();
}
if (in_joystick_x < x_lowerTrigger){
setRegisterPin(4,LOW);
setRegisterPin(5,HIGH);
analogWrite(x_LED, map(in_joystick_x,x_upperTrigger,0,0,255));
writeRegisters();
}
if (in_joystick_x > x_lowerTrigger && in_joystick_x < x_upperTrigger){
setRegisterPin(4,LOW);
setRegisterPin(5,LOW);
analogWrite(x_LED,0);
writeRegisters();
}
// x above y below
if (in_joystick_y > y_upperTrigger){
setRegisterPin(2,HIGH);
setRegisterPin(3,LOW);
analogWrite(y_LED, map(in_joystick_y,y_upperTrigger,1023,0,255));
writeRegisters();
}
if (in_joystick_y < y_lowerTrigger){
setRegisterPin(2,LOW);
setRegisterPin(3,HIGH);
analogWrite(y_LED, map(in_joystick_y,y_upperTrigger,0,0,255));
writeRegisters();
}
if (in_joystick_y > y_lowerTrigger && in_joystick_y < y_upperTrigger){
setRegisterPin(2,LOW);
setRegisterPin(3,LOW);
analogWrite(y_LED,0);
writeRegisters();
}
//outputs
brightness = brightness + fadeAmount;
// reverse the direction of the fading at the ends of the fade:
if (brightness == 0 || brightness == 255) {
fadeAmount = -fadeAmount ;
}
out_ref = readMux(15);
out_pot1 = readMux(0);
out_pot2 = readMux(1);
out_accelerometer_x = readMux(2);
out_accelerometer_y = readMux(3);
out_accelerometer_z = readMux(4);
out_temp1 = readMux(5);
xbee_serial.print(out_ref);
xbee_serial.print(",");
xbee_serial.print(brightness);
xbee_serial.print(",");
xbee_serial.print(out_pot1);
xbee_serial.print(",");
xbee_serial.print(out_pot2);
xbee_serial.print(",");
xbee_serial.print(out_accelerometer_x);
xbee_serial.print(",");
xbee_serial.print(out_accelerometer_y);
xbee_serial.print(",");
xbee_serial.print(out_accelerometer_z);
xbee_serial.print(",");
xbee_serial.print(out_temp1);
xbee_serial.print("."); //EOP marker
delay(10);
}
// for substring
char* subStr (char* input_string, char *separator, int segment_number) {
char *act, *sub, *ptr;
static char copy[MAX_STRING_LEN];
int i;
strcpy(copy, input_string);
for (i = 1, act = copy; i <= segment_number; i++, act = NULL) {
sub = strtok_r(act, separator, &ptr);
if (sub == NULL) break;
}
return sub;
}
// for mux
int readMux(int channel){
int controlPin[] = {s0, s1, s2, s3};
int muxChannel[16][4]={
{0,0,0,0}, //channel 0
{1,0,0,0}, //channel 1
{0,1,0,0}, //channel 2
{1,1,0,0}, //channel 3
{0,0,1,0}, //channel 4
{1,0,1,0}, //channel 5
{0,1,1,0}, //channel 6
{1,1,1,0}, //channel 7
{0,0,0,1}, //channel 8
{1,0,0,1}, //channel 9
{0,1,0,1}, //channel 10
{1,1,0,1}, //channel 11
{0,0,1,1}, //channel 12
{1,0,1,1}, //channel 13
{0,1,1,1}, //channel 14
{1,1,1,1} //channel 15
};
//loop through the 4 sig
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i ++){
digitalWrite(controlPin[i], muxChannel[channel][i]);
}
//read the value at the SIG pin
int val = analogRead(SIG_pin);
//return the value
return val;
}
// for shift registers
void clearRegisters(){
for(int i = numOfRegisterPins - 1; i >= 0; i--){
registers[i] = LOW;
}
}
// for shift registers
void writeRegisters(){
digitalWrite(RCLK_Pin, LOW);
for(int i = numOfRegisterPins - 1; i >= 0; i--){
digitalWrite(SRCLK_Pin, LOW);
int val = registers[i];
digitalWrite(SER_Pin, val);
digitalWrite(SRCLK_Pin, HIGH);
}
digitalWrite(RCLK_Pin, HIGH);
}
//set an individual pin HIGH or LOW
void setRegisterPin(int index, int value){
registers[index] = value;
}
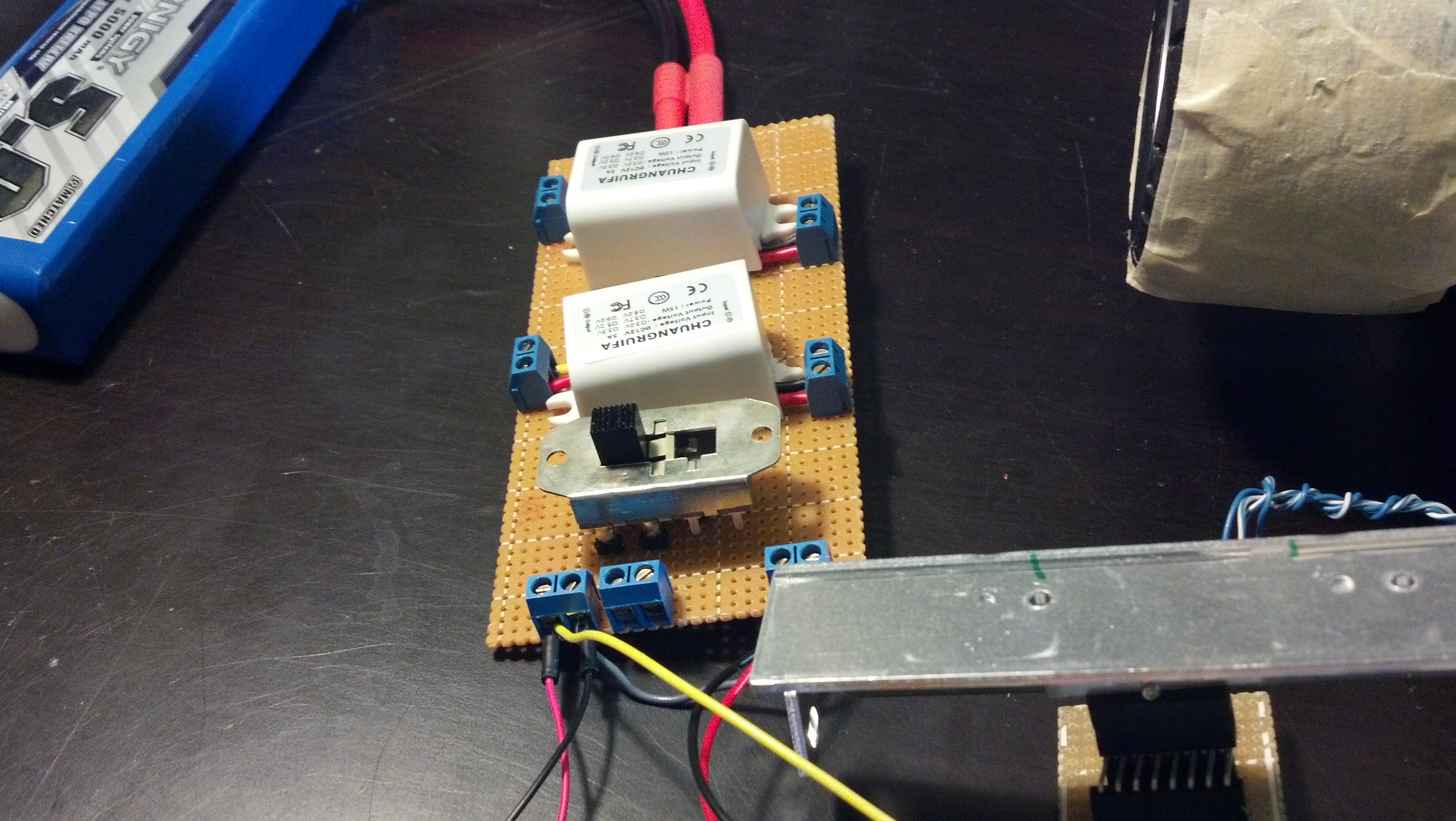
Like I promised in the video, here are a few more properly focused pictures: